Maintaining healthy ears and healthy hearing is an essential aspect of overall well-being. Impacted wax in the ear canal can cause decreased hearing and discomfort. For hearing aid users, ear wax management is arguably even more important as wax can clog up a user’s hearing aid and cause it to stop working. This blog will shed light on the importance of proper ear wax management and provide you with a comprehensive guide to safe and effective ear wax removal techniques.
The Role of Ear Wax
Before we delve into removal techniques, it’s crucial to understand the role ear wax, or cerumen, plays in our ears. Ear wax is a natural substance produced by the body to protect the delicate ear canal from dust, debris, and foreign invaders. It acts as a defense mechanism, preventing infections and maintaining an optimal environment for hearing. However, an excessive accumulation of ear wax can lead to discomfort, temporary hearing loss, and other complications. Thus, knowing when and how to remove excess ear wax is of utmost importance.
When to Seek Ear Wax Removal
Not all instances of ear wax accumulation require removal. Our ears are generally quite adept at self-cleaning, with older wax being pushed out of the ear canal naturally. However, if you experience any of the following symptoms, it might be time to consider ear wax removal:
- Gradual hearing loss or muffled sounds
- Earache or discomfort
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Dizziness or imbalance
- Itching or irritation
Safe Ear Wax Removal Techniques
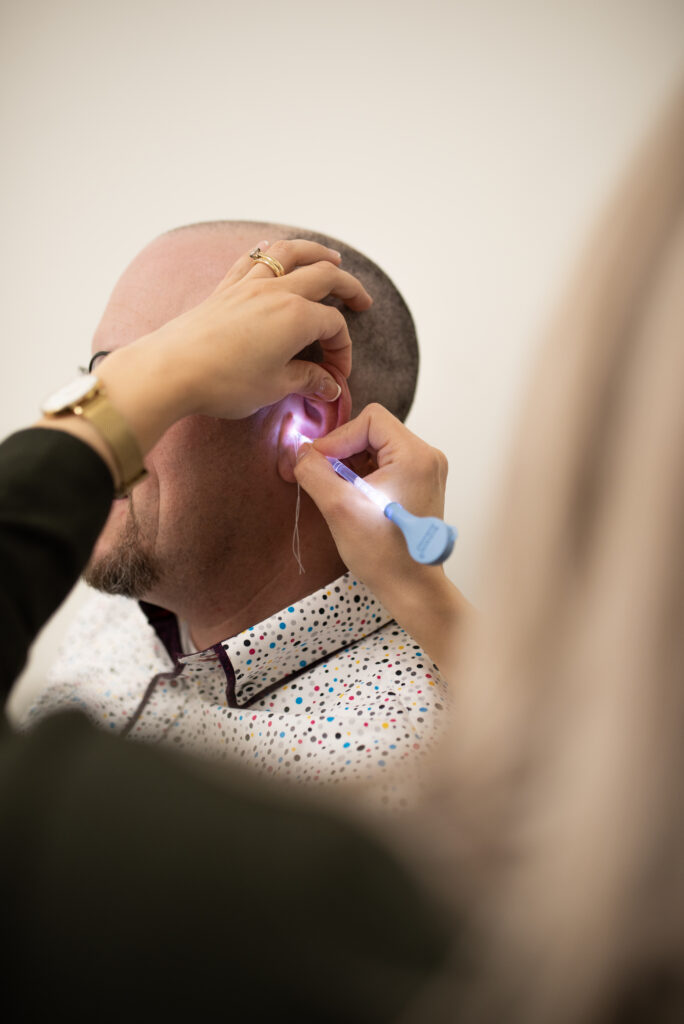
As an audiologist, I always recommend prioritizing safe and gentle techniques when it comes to ear wax removal. Here are some tried-and-true methods:
- Mineral Oil or Baby Oil: Applying a few drops of mineral oil or baby oil to the ear canal can help soften ear wax over a few days, making it easier to remove. This at-home technique is recommended most often for children and adults as a first step. Remember, never insert objects like cotton swabs or hairpins into the ear canal, as this can push the wax deeper and potentially cause injury.
- Over-the-Counter Ear Drops: For heavily impacted and/or hardened ear wax, non-prescription ear drops designed for wax removal can help soften the wax, making it easier to expel. Ear drops containing the active ingredient carbamide peroxide are typically most effective. However, it’s crucial to follow the instructions carefully and avoid using drops if you suspect any ear injury, ear drum perforation, or infection.
- Irrigation: This method involves using warm water and a bulb syringe to gently flush softened wax out the ear canal. Kits can be purchased at your local pharmacy. Tilt your head and pull your outer ear up and back to straighten your ear canal. When finished irrigating, tip your head to the side to let the water drain out. It’s essential to ensure the water is at body temperature and to direct the flow of water toward the ear canal’s wall, rather than directly at the eardrum. While this at-home technique can be very effective, it can also sometimes push the ear wax deeper into the ear canal making removal by a professional more difficult and uncomfortable. ***At home irrigation is not recommended on infants or children.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are unsure about the proper method or if your symptoms persist, it’s always best to consult a registered audiologist who is formally trained in ear wax removal. They can assess your ear health and if necessary, use special tools and techniques, such as suction, curettage, or forceps to safely remove excessive ear wax.
More information on our ear wax removal services and fees.
Preventing Future Build-Up
To minimize the need for frequent ear wax removal, consider these preventive measures:
- Avoid Over-Cleaning: Cleaning the ears excessively can disrupt the natural wax migration process. Gently wipe the external ear with a damp cloth and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
- Limit Water Exposure: Excessive moisture can lead to softened wax, increasing the risk of impaction. Use earplugs while swimming, diving, or showering, especially in stagnant or unclean water.
- Regular Check-ups: Periodic visits to your registered audiologist can help monitor your ear health and ensure that any wax accumulation is detected early and managed appropriately.
Conclusion
As a registered audiologist, my priority is your ear health and overall well-being. While ear wax removal is an essential aspect of maintaining healthy ears, it’s equally crucial to prioritize safe and effective techniques. By understanding the role of ear wax, knowing when to seek removal, and adopting preventive measures, you can enjoy optimal hearing and minimize the risk of complications. Remember, when in doubt, always consult a registered audiologist to ensure the best care for your ears.
Schedule an ear wax removal appointment with our clinic today if you or a loved one are suffering from impacted ear wax.

Blog Author
Lyndsay Bozec
REGISTERED AUDIOLOGIST, NSCASLP
Lyndsay is a passionate advocate for hearing health awareness and hearing preservation. Over the years she has delivered various hearing health presentations and hearing aid workshops for caregiver workshops across HRM.
